Hazard Analysis & Critical Control Points (HACCP)
HACCP is a management
system in which food safety is addressed through the analysis and control
of biological, chemical, and physical hazards from raw material production, procurement and handling,
to manufacturing, distribution and consumption of the finished product.
Planning and integration of a HACCP concept and management including daily work templates for employees in the F & B department.
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points (HACCP) is an internationally recognized method of identifying and managing food safety related risk and, when central to an active food safety program, can provide your customers, the public, and regulatory agencies assurance that a food safety program is well managed. HACCP is a management system in which food safety is addressed through the analysis and control of biological, chemical, and physical hazards from raw material production, procurement and handling, to manufacturing, distribution and consumption of the finished product. Through analysis of hazards and where they can occur, controlling and templates helps implement systems and procedures to minimize risk. Work-sheets of a safety management system will help at each and every operation in assisting in the management of critical control points.
A food safety program, however, does not just stop with HACCP.
To be effective, prerequisite programs such as pest control, traceability & recall, hygiene and sanitation need to be developed and implemented. Additionally, the issue of ensuring that suppliers and distributors also have a food safety program needs to be addressed through development of ingredient specifications and a vendor assurance system.
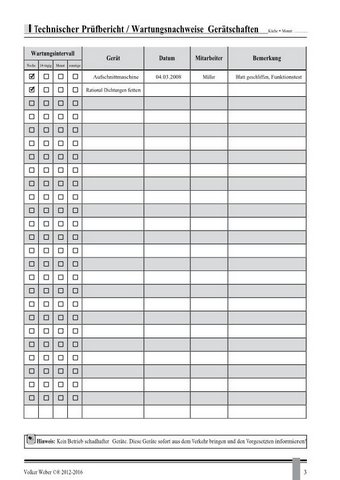
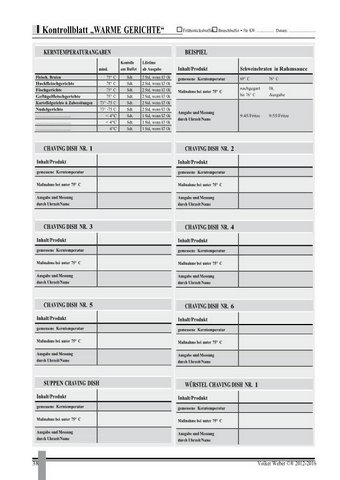
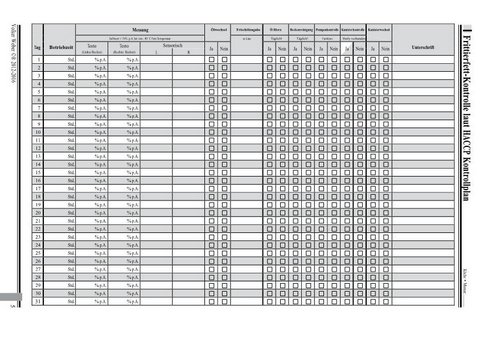
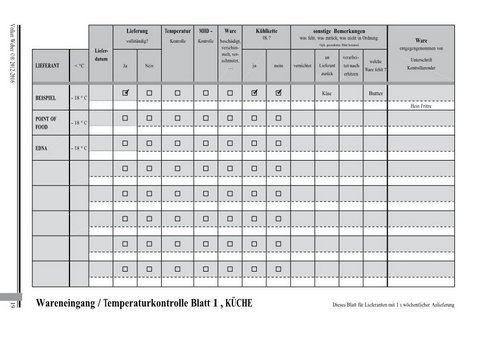
This is an example of a HACCP manual that i wrote for a German company. It includes the
legal framework and templates for daily use by the employees.
Principle 1 - Conduct a Hazard Analysis
.The
application of this principle involves listing
the steps in the process and identifying where
significant hazards are likely to Occur. The
HACCP team will focus on hazards that can be
prevented, eliminated or controlled by the HACCP
plan. A justification for including or excluding
the hazard is reported and possible control
measures are identified.
Principle 2 - Identify the Critical Control Points
.A critical control
point (CCP) is a point, step or procedure at
which control can be applied and a food safety
hazard can be prevented, eliminated or reduced
to acceptable levels. The HACCP team will use a
CCP decision tree to help identify the critical
control points in the process. A critical
control point may control more that one food
safety hazard or in some cases more than one CCP
is needed to control a single hazard. The number
of CCP's needed depends on the processing steps
and the control needed to assure food safety.
Principle 3 - Establish Critical Limits
.A
critical limit (CL) is the maximum and/or
minimum value to which a biological, chemical,
or physical parameter must be controlled at a
CCP to prevent, eliminate, or reduce to an
acceptable level the occurrence of a food safety
hazard. The critical limit is usually a measure
such as time, temperature, water activity (Aw),
pH, weight, or some other measure that is based
on scientific literature and/or regulatory
standards.
Principle 4 - Monitor CCP
.The HACCP
team will describe monitoring procedures for the
measurement of the critical limit at each
critical control point. Monitoring procedures
should describe how the measurement will be
taken, when the measurement is taken, who is
responsible for the measurement and how
frequently the measurement is taken during
production.
Principle 5 - Establish Corrective
Action .Corrective actions are the procedures
that are followed when a deviation in a critical
limit occurs. The HACCP team will identify the
steps that will be taken to prevent potentially
hazardous food from entering the food chain and
the steps that are needed to correct the
process. This usually includes identification of
the problems and the steps taken to assure that
the problem will not occur again.
Principle 6 -
Verification
.Those activities, other than
monitoring, that determine the validity of the
HACCP plan and that the system is operating
according to the plan. The HACCP team may
identify activities such as auditing of CCP's,
record review, prior shipment review, instrument
calibration and product testing as part of the
verification activities.
Principle 7 -
Recordkeeping
.A key component of the HACCP plan
is recording information that can be used to
prove that the a food was produced safely. The
records also need to include information about
the HACCP plan. Record should include
information on the HACCP Team, product
description, flow diagrams, the hazard analysis,
the CCP's identified, Critical Limits,
Monitoring System, Corrective Actions,
Recordkeeping Procedures, and Verification
Procedures. HACCP Does not Stand Alone! The
application of HACCP does not stand alone in a
food processing facility. The plan must be built
on other food safety programs. Good
Manufacturing Practices (GMP) that are practiced
by the processing facility will support HACCP
plan and will address food safety and food
quality issues that are not critical for the
reduction of food safety hazards. Sanitation
Standard Operating Procedures (SSOP's) are
required in federally inspected meat and poultry
operations and address procedures for clean
facilities, equipment and personnel that are
necessary for all products produced in a
facility.
Check out this sample files
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
| Final HACCP Book | HACCP working sheets | |||
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
.jpg) |
 |
 |